Contents
What are arthritic conditions (arthritis)?
Arthritis is a chronic condition that causes inflammation in the joints, leading to pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility.
Around 10 million people in the UK have arthritic conditions. Although it is more common in people aged over 65, the condition can affect young adults, children and even animals.
Living with arthritic conditions can affect a person’s mental and emotional wellbeing significantly, however, the condition doesn’t have to be a life sentence. There are many treatment options available to help manage the symptoms of arthritis and improve quality of life.
What are the different types of arthritis?
Broadly, arthritis can be divided into two types of arthritic conditions – degenerative and inflammatory.
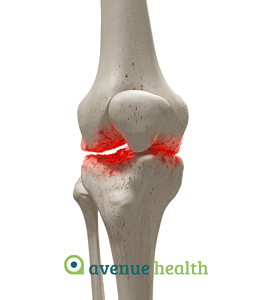
Degenerative arthritis or osteoarthritis – sometimes also called ‘wear and tear’ – is the most common form of arthritis. Indeed, it is caused by gradual ‘wear and tear’ of the cartilage that cushions our joints. Cartilage is a firm, rubbery tissue that covers the ends of bones in a joint, allowing for smooth movement and absorbing shock. In osteoarthritis, the cartilage gradually breaks down, causing the bones in the joint to rub against each other, leading to pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility.
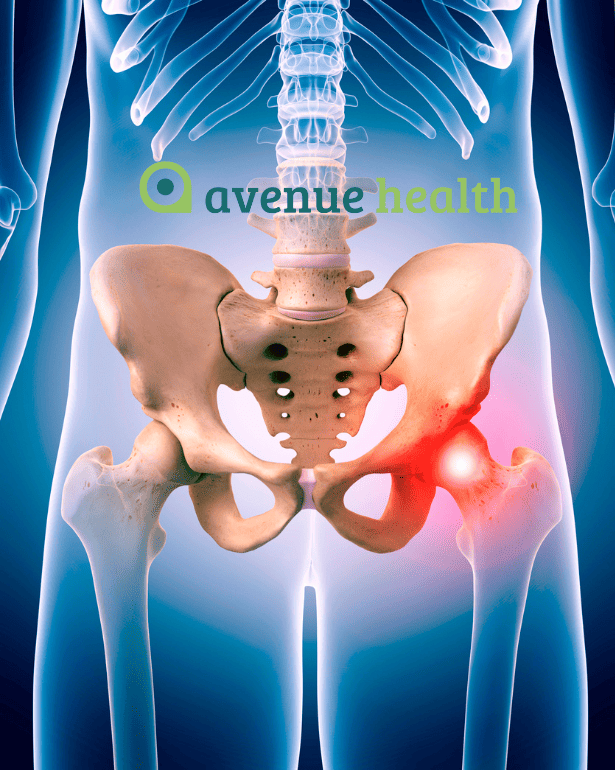
Degenerative arthritis or osteoarthritis is usually localised to a specific site such as the hips, knees or spine. It is more common in women.
On the other hand, inflammatory arthritis, such as rheumatoid arthritis, is an autoimmune disease affecting not just individual joints, but whole areas of the body. In simple terms, autoimmune diseases are when the immune system – which usually fights off infection – attacks healthy cells in the body by accident.
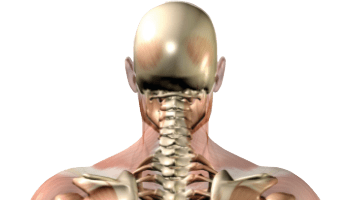
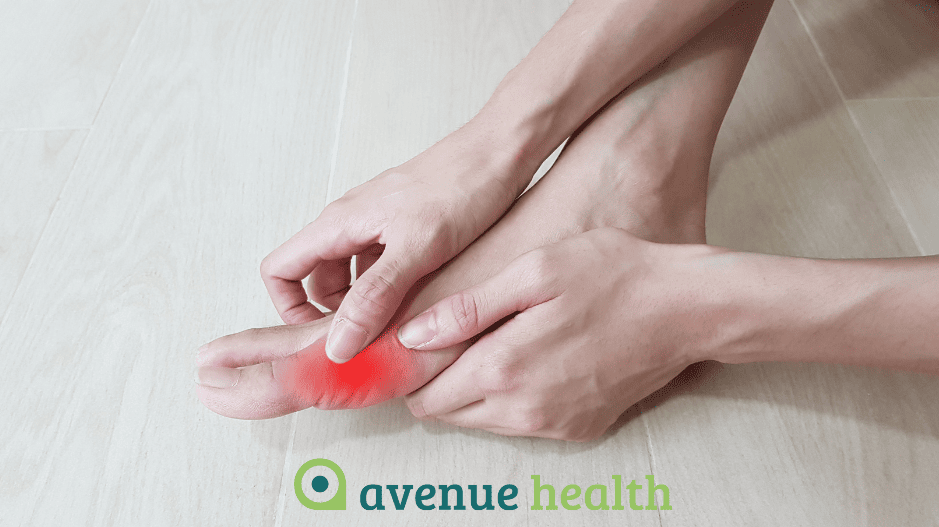
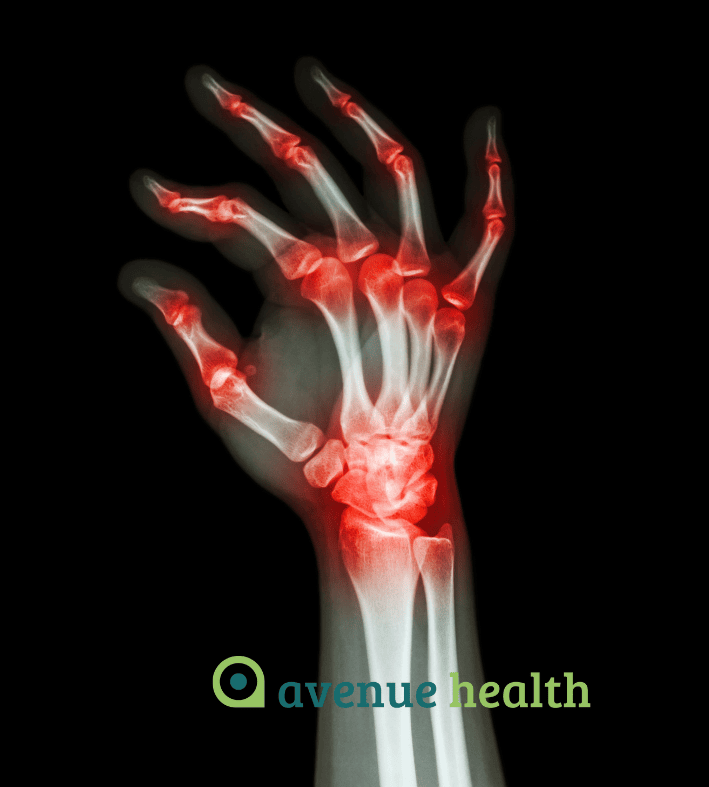
Rheumatoid arthritis most commonly affects the hands and feet first. Like osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis produces severe pain, stiffness and deformity in affected areas (e.g. hammer toe). This form of arthritis is less suitable for manual therapy and responds better to the correct medication.
Other forms of arthritic conditions can be found listed on the NHS website.
What are some symptoms of arthritis?
Look for these tell-tale signs if you suspect you may be suffering from arthritic conditions.
- Pain in your joints. This pain may be mild or severe, and constant or intermittent.
- Stiffness in the joints. Especially in the morning or after long periods of inactivity.
- Swelling. Arthritis can cause swelling in the joints, which may be accompanied by warmth and redness.
- Limited mobility. As arthritis progresses, it can limit the range of motion in the affected joints, making it difficult to perform everyday activities. For example, those who have arthritis in their hands may find it difficult to grip objects.
- Fatigue. Some people with arthritis may experience fatigue, which can be caused by the body’s immune response to the inflammation.
- Deformities. In severe cases, arthritis can cause deformities in the joints, such as knobby finger joints or misaligned joints in the hips or knees.

Can We Help Your Arthritis?
Osteopathic treatment can do a great deal to reduce pain, ease swelling and improve mobility and range of joint movement. Our approach to treating arthritic conditions is aimed at reducing inflammation by using gentle, manual techniques on joints, muscles and ligaments.
Get a 30-minute new patient assessment, diagnosis & treatment plan for just £35
Will Pain-Relieving Drugs Help?
Inflammation caused by arthritis can be greatly reduced with the use of NSAID (Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs), such as ibuprofen, aspirin and paracetamol. Although they can reduce the inflammation caused by your problem, they do not address the underlying problem of your arthritis. They can, in some cases, cause stomach problems, such as acid reflux and constipation. It is important not to use painkilling drugs before engaging in physical activity. This is because, without feedback from your body’s nervous system, it is easy to over-use and further aggravate your condition.
However, they are very useful in helping you get a good night’s sleep, which is a vitally important part of your recovery. If you are already taking medication prescribed by a doctor, you should always ask the advice of a Doctor or Pharmacist before self-medicating, as some pain-killing drugs can affect the effectiveness of your medication, and can sometimes be dangerous.